- Structure of Measles Virus-
- Measles virus is a member of the genus Morbillivirus of the family Paramyxoviridae
- Measles) virus is a typical paramyxovirus (spherical enveloped particles that contain a non segmented negative strand RNA genome)
- Measles virus have two types of envelope spikes that shows:

Hemagglutinating activity
Cell fusion and hemolytic activity
- Single serotype i.e. Life long immunity occurs in individuals who have had the disease.
- Hemagglutinin is the antigen against which neutralizing antibody is formed.
- Infants are protected during the first six months of life ( they get maternal antibody as it passes the placenta)
Replication cycle of Measles Virus
- Adsoprtion to the cell surface: via Hemagglutinin. Cellular receptor of measles virus is CD46 molecule.
- Penetrates the cell surface and uncoats
- Virion RNA polymerase transcribes the negative-strand genome to mRNA
- Specific viral proteins are formed
- Assembly to helical nucleocapsid
- Release of virus by budding
Transmission and Epidemiology of Measles
- Worldwide distribution, outbreaks in 2-3 years
- Transmitted via respiratory droplets produced by sneeze or cough during prodromal period which continues up to few days after rash appears
- Measles virus is extremely infectious, most children contract clinical disease on exposure
- More serious outcomes in Malnurished children, people with deficient cell mediated immunity.
Pathogenesis
- Measles virus infects the cells lining the upper respiratory tracts
- Enters blood and infects reticuloendothelial cells and replicates again.
- Spread to skins
- Appearances of rash: (because of cytotoxic T cells attacks measles virus infected vascular endothelial cells in the skin).
- Formation of Multinucleated giant cells.
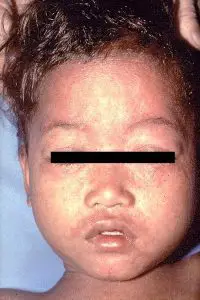
Clinical features of Measles
- Incubation period: 10-14 days
- Prodromal phase: Characterized by fever, conjunctivitis (causing photophobia), running nose, and coughing
- Appearance of Koplik’s spot (bright red lesions with the white, central dot) # Diagnostic feature
- Appearance of Maculopapular rashes, common features of which includes:
- Occurs 5‐7 days after symptoms
- Lasts 3 or more days
- Brownish hue
- Progresses from face to body to extremities
- Rash becomes confluent as it progresses
- Rash affects palms and soles
- Soon after the rash appears, the patient is no longer infectious.
Complications because of Measles infections
- Encephalitis: 1 per 1000 cases
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE): Fatal disease of nervous system can develop after several years after measles.
- Giant cell pneumonia
- Co-infections:
– Secondary bacterial pneumonia – Bacterial otitis media
- Increased risk of still birth in pregnant women infected with measles.
- Measles virus infection of fetus causes fetal death
- Atypical measles develops in some people who were given killed vaccine and subsequently infected with measles virus.
No comments:
Post a Comment